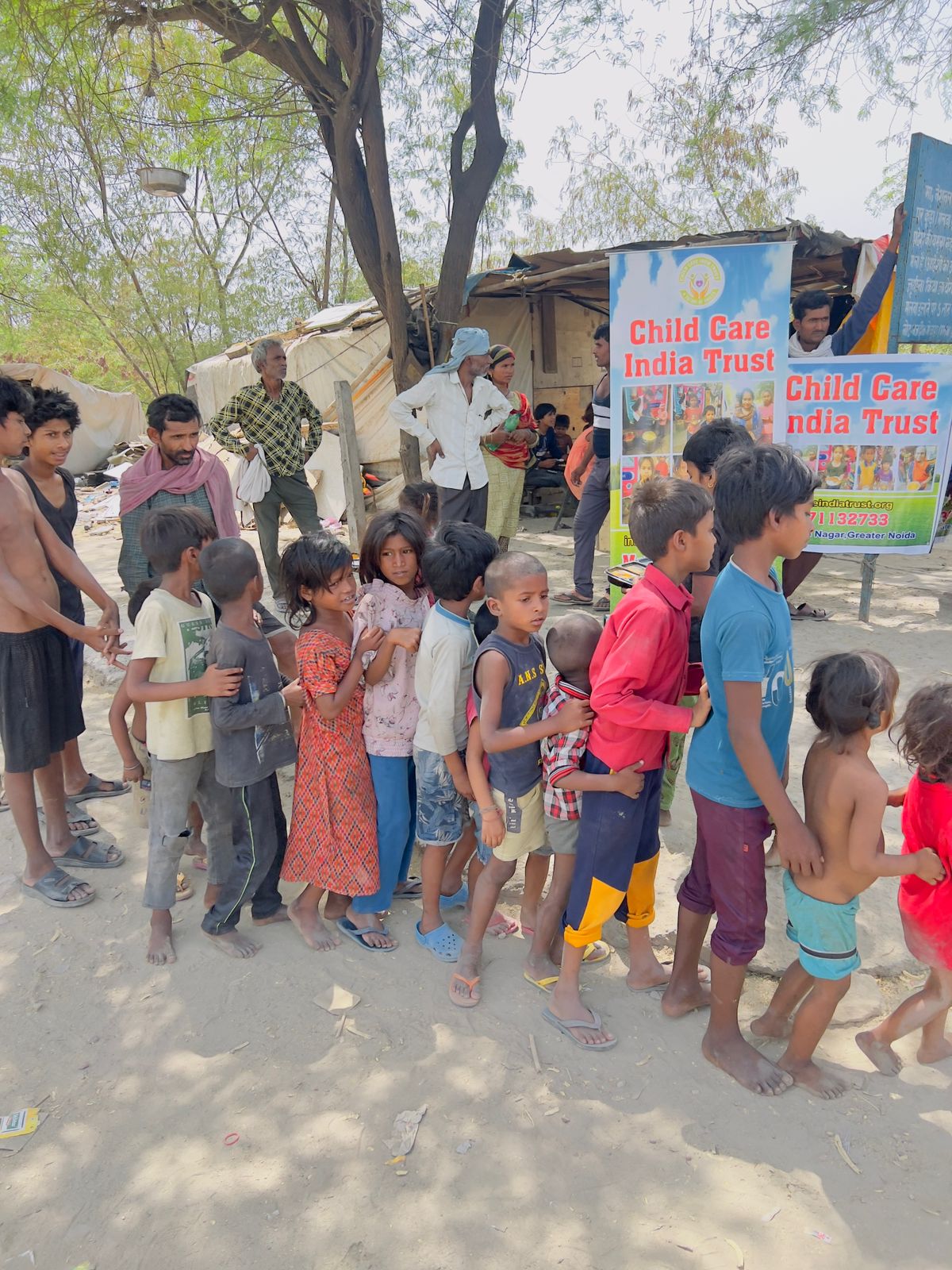
Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress
Millions of Indians struggle to meet their basic requirements, including food, shelter, healthcare, and education, making poverty one of the country’s most urgent problems. The nation has experienced tremendous economic growth in recent decades, but a sizable section of the populace still lives in poverty. But despite these obstacles, there are numerous avenues for advancement that can lessen India’s poverty. The causes, effects, and remedies of poverty in India will be discussed in this article, with an emphasis on the difficulties as well as the initiatives being taken to further inclusivity and progress, childcareindiatrust.
The Root Causes of India’s Poverty
India’s history, socioeconomic structure, and political dynamics are all intricately linked to the country’s poverty. Among the main reasons are:
1. Economic Inequality
Extreme poverty and extreme riches coexist in India, where the gap between the rich and the poor is widening. Due to a number of issues, including unequal resource distribution, a concentration of wealth in specific economic sectors, and a lack of employment prospects for excluded populations, economic inequality has gotten worse over time. Disadvantaged groups’ economic mobility is frequently restricted by this inequality, which feeds the poverty cycle, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
2. Rural Poverty and Agrarian Crisis
A sizable section of India’s population resides in rural regions, which have very high rates of poverty. Low agricultural output and insufficient income for farmers have resulted from agrarian distress brought on by elements including inadequate irrigation, antiquated farming methods, and climate change. The situation is made worse by the fact that rural areas frequently lack access to basic amenities including infrastructure, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress. healthcare, and education, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
3. Lack of Education and Skill Development
A key component of ending the cycle of poverty is education. Unfortunately, a lot of kids lack access to high-quality education, particularly in rural areas. Their future career and personal growth prospects are restricted by this lack of education. Furthermore, many people are left unprepared for the modern workforce by insufficient skill development programs, which keeps them in poverty, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
4. Unemployment and Underemployment
India’s unemployment rate is still high despite the country’s expanding economy, especially for young people and those from disadvantaged backgrounds. Another prevalent problem is underemployment, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress which occurs when people work in low-wage, precarious positions that do not fully utilize their skills. Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress Many are forced to accept low pay or stay unemployed due to a lack of suitable employment possibilities in important industries including manufacturing, services, and agriculture. Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
5. Discrimination Based on Social and Caste
For many segments of Indian society, especially the Dalits and Adivasis, caste-based discrimination continues to be a major obstacle to social and economic mobility. The cycle of poverty is sustained by the discrimination these populations frequently experience in the workplace, in school, and in access to essential services. The problem is made worse by gender inequality, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress which makes it harder for women to access resources and opportunities.
The Effects of India’s Poverty
The effects of poverty in India are extensive and have a significant influence on people, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress families, and society as a whole. Among the most notable consequences are:
1. Health Issues and Problem
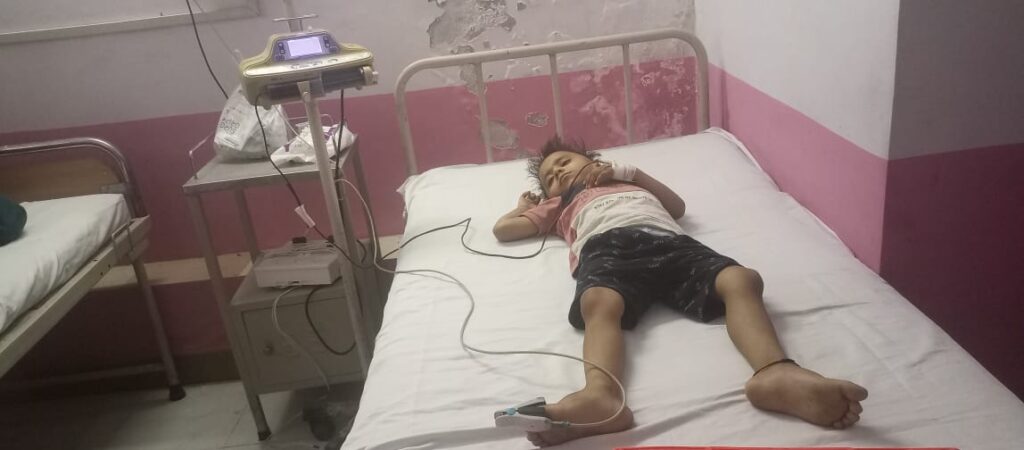
In India, poverty and poor health outcomes are tightly related. High rates of child mortality, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress malnutrition, and the spread of avoidable diseases are caused by a lack of access to sanitary facilities, clean water, and healthcare services. Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress Malnutrition causes immune system weakness, limited growth, and long-term developmental difficulties, especially in children, trust. Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
2. Limited Access to Education
Poverty prevents many children from receiving a proper education, leading to illiteracy and low skill levels. Without education, individuals are less likely to find well-paying jobs, perpetuating the cycle of poverty. Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress Furthermore, children from impoverished backgrounds often face pressure to enter the workforce at an early age, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress further limiting their educational opportunities.
3. Social Instability and Crime
High levels of poverty often contribute to social instability, as individuals who feel marginalized and disenfranchised may resort to crime, violence, and other forms of social unrest, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress. This instability can hinder economic development, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress as businesses may be reluctant to invest in areas that are perceived as unsafe or unstable Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
4. Gender Inequality
Women who live in poverty frequently experience higher rates of discrimination, exploitation, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress and gender-based violence. The gender gap in sectors like healthcare, education, and economic engagement is made worse by poverty, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress. Women in low-income homes are less likely to have access to resources that could enhance their quality of life and frequently have little say in decisions.
Paths to Progress: Tackling Poverty in India
Even though there are many obstacles to overcome, there are many programs and tactics designed to reduce poverty and encourage inclusive growth. Government and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) work together on these avenues for advancement, and the business sector contributes creative solutions as well. Key tactics consist of.
1. Programs for Social Welfare and Government Schemes
To improve the lives of the impoverished, the Indian government has started a number of initiatives to reduce poverty. Among the most important schemes are:
- Mantri Pradhan PMJDY, or Jan Dhan Yojana: In order to encourage savings and financial security, this financial inclusion program seeks to open bank accounts for all Indian households, especially those in rural areas.
- The National Rural Employment Guarantee Act of Mahatma Gandhi (MGNREGA): This initiative ensures that the poorest families have a source of income by giving rural households guaranteed employment for a minimum of 100 days annually,Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
- The National Health Mission (NHM) program seeks to give impoverished communities in both rural and urban areas access to reasonably priced healthcare services.
- The Midday Meal Scheme lowers malnutrition and promotes education by guaranteeing that kids in public schools eat wholesome meals.
2. Promoting Inclusive Education and Skill Development
Education and skill development are critical for breaking the poverty cycle. Initiatives such as the Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA) and Skill India Mission are aimed at improving access to education and equipping young people with the necessary skills to succeed in the job market. By focusing on vocational training, entrepreneurship, and digital literacy, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress. these programs create opportunities for individuals to improve their socio-economic status,Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
3. Empowering Women and Marginalized Groups
Reducing poverty and advancing gender equality require the empowerment of women and marginalized groups. Initiatives like Stand Up India, which offers financial assistance to female entrepreneurs, and Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, which attempts to close , Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress. the gender gap in education, are positive advances. Furthermore, a number of NGOs strive to advance social justice and give underprivileged populations, such Dalits and Adivasis, access to resources.
4. Promoting Long-Term Economic Development
Only until economic possibilities are distributed throughout all areas and industries will India’s economy be able to grow inclusively. The rural-urban divide will be lessened and jobs will be created by supporting small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs), investing in rural infrastructure, and promoting sustainable farming methods. Initiatives for financial inclusion, like microfinance, can also help entrepreneurs from underprivileged areas launch their own companies and escape poverty,Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress.
5. Reducing Inequality through Tax Reforms
Economic disparity can be lessened by implementing progressive tax laws that target the wealthy and redistribute wealth. In order to give the underprivileged and vulnerable groups a safety net, the government can also boost spending in areas like social security, Poverty in India Challenges and Paths to Progress. healthcare, and education.
In conclusion, creating a better future for everybody
India’s poverty problem is complicated and calls for all-encompassing, multifaceted solutions. Even though there has been a lot of success in combating poverty, much more work has to be done. India can create a more promising future for its people by emphasizing inclusive growth, empowering underprivileged groups, and guaranteeing access to healthcare and education. To eradicate poverty and create a more just and equal society, cooperation between the public and private sectors will be essential.
Strengthening Infrastructure to Support Rural Communities
Infrastructure building actually delays poverty reduction, especially in rural areas. In this regard, most of the villages have minimal facilities for essential services, making it hard for villages to promote their people for healthcare, education, and transportation. If these roads, electricity, sanitation, and internet supply are improved, the government can make sure that economic opportunities flourish for the poor in the rural areas.
1. Rural Electrification and Energy Access
Unreliable or disconnected electrical supplies are one of the biggest obstacles to energy access for many Indian rural families. Actually, the government is currently putting a lot of effort into giving rural areas a steady, round-the-clock supply of power through programs like the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY). Better healthcare, education, and information access, among other digitally accessible services essential for economic growth, are all made possible by having access to energy.
2. Rural Health Infrastructure
Unconnected or inconsistent electrical supplies are one of the biggest obstacles to energy access for many rural homes in India. The government actually places a lot of emphasis on supplying energy to rural areas around-the-clock through programs like the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY). Through improved healthcare, education, and information access, among other digitally accessible services essential for economic growth, access to electricity raises living standards.
3. Expanding Connectivity through Digital Platforms
Internet access has become an essential tool for business, education, and healthcare in the current technological era. By bringing internet connectivity to rural areas, programs like Digital India and the BharatNet Project open the door to e-learning, telemedicine, and e-commerce. By equipping people with digital skills and online resources, it promotes social and economic inclusion and closes the gap between those who are digitally privileged and those who are not.
The Function of Social Entrepreneurship and Microfinance
Since the banks were having trouble reaching the poorest segments of Indian society to provide their customary services, this was also an innovative instrument for reducing poverty. Microfinance institutions, for instance, helped break the cycle of poverty by giving women who could not access conventional banks small loans that they could use to start small companies and raise their standard of living.
1. Women’s Empowerment through Microfinance
By giving them the capital to launch their own companies or supplement family income, microfinance plays a critical role in empowering women. In rural India, initiatives like Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have proven especially effective since they give women a sense of belonging and financial support. These initiatives provide low-interest loans and financial education to enable women to start their own businesses and become more financially independent.
2. Social Entrepreneurship for Sustainable Development
Social entrepreneurship is another area through which the issue of poverty in India is being addressed. Social enterprises deal with sustainable solutions to social issues like unemployment, poor health, and lack of education. The enterprises often take place in unprivileged regions, dealing with direct issues affecting the poor, including access to clean energy, health care, and housing. Social entrepreneurship would, therefore, provide India with an opportunity to bring in innovative solutions to the problems of poverty while also driving economic growth and development.
Utilizing Technology to Reduce Poverty
An increasingly effective weapon in the fight against poverty is technology. Addressing the underlying causes of poverty in India is becoming simpler because to technical advancements like digital payments, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI).
1. Digital Financial Inclusion
Digital financial services, such as mobile banking and payment systems, have made it possible for millions of low-income families in rural areas to access basic banking services. Programs like Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and Aadhaar-based Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) are helping ensure that subsidies and welfare benefits reach the right beneficiaries without middlemen, reducing corruption and ensuring that the poor can access financial services efficiently.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Big Data for Focused Solutions
Through the use of big data and AI, policymakers will be able to understand the needs of the poor better and create targeted interventions based on specific issues that marginalized communities face. For instance, AI can be used to create predictive models that allow governments to know which areas are most poverty-ridden, determine the effectiveness of existing programs, and allocate resources more effectively. Technology can also help in enhancing the monitoring and evaluation of poverty alleviation programs to ensure that they yield tangible results.
The Importance of Global Partnerships and Collaboration
The majority of India has abolished poverty, yet it is still too much for any one organization to bear on its own. To accelerate progress, this necessitates the collaboration of private sector companies, NGOs, and international organizations. International donors, the World Bank, and the United Nations Development Programme can all provide financial and technical support for large-scale initiatives aimed at reducing poverty.
1. International Aid and Development Programs
India still receives aid from outside for a variety of programs aimed at reducing poverty, especially in areas like education, healthcare, and nutrition. International organizations’ assistance is essential to making sure these initiatives are successful, expandable, and long-lasting.
2. Private Sector Engagement in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
The private sector in India is also increasingly investing in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives that focus on poverty reduction. Many corporations contribute to building social infrastructure, funding education programs, and supporting healthcare initiatives. By collaborating with NGOs and government agencies, businesses can ensure that their CSR efforts reach the most vulnerable populations and have a long-term impact on poverty alleviation.
Conclusion: A Shared Accountability for a Successful Future
Poverty in India is a multi-dimensional challenge requiring action from both the government, social innovation, economic reforms, and international cooperation. Though many of the earlier problems have started to show promise of improvement, there is much still to be done to guarantee that every Indian has access to resources and opportunities necessary for decent living standards. By focusing on inclusive growth, improving education, empowering marginalized communities, and utilizing technology, India can create a future where poverty is no longer a barrier to opportunity and prosperity.
Together, we can create lasting change and build a more equitable society where all citizens, regardless of their background or location, can thrive.



